Understanding the lifecycle of bacteria that cause thrush is essential for effectively managing and treating this common infection. Thrush is a type of yeast infection caused by the overgrowth of the Candida fungus in the mouth and throat.
This condition can be uncomfortable and even painful, making it important to understand how these bacteria behave over time. By gaining insight into the lifecycle of thrush-causing bacteria, researchers and healthcare providers can develop more targeted and efficient approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
In this article, we will explore the stages of the lifecycle of these bacteria and how they contribute to the development and persistence of thrush infections.
1. Introduction to Thrush-Causing Bacteria

Thrush-causing bacteria are a diverse group of microorganisms that can thrive in various environments, including the human body. These bacteria are responsible for causing oral thrush, a common fungal infection characterized by white patches on the mouth, tongue, and throat.
Understanding the lifecycle of thrush-causing bacteria is essential for developing effective treatment strategies to combat this infection. Through a combination of scientific research and clinical studies, scientists have been able to shed light on the intricate processes that these bacteria undergo to survive and proliferate in the human body.
By delving into the mechanisms by which these bacteria interact with their environment and host, we can gain valuable insights into how to better manage and prevent thrush infections.
2. The Life Cycle of Thrush-Causing Bacteria

The life cycle of thrush-causing bacteria is a complex and varied process that involves multiple stages. The bacteria begin their life cycle as dormant spores, waiting for the right conditions to germinate and grow.
Once activated, they begin to multiply rapidly, colonizing the affected area and causing inflammation and irritation. As they continue to reproduce, the symptoms of thrush become more pronounced, with itching, burning, and white patches appearing on the skin or mucous membranes.
Over time, the bacteria may spread to other parts of the body if left untreated, causing secondary infections and potentially serious health issues. Understanding the life cycle of these bacteria is essential for developing effective treatments and prevention strategies.
3. Factors Influencing the Growth and Spread of Thrush-Causing Bacteria
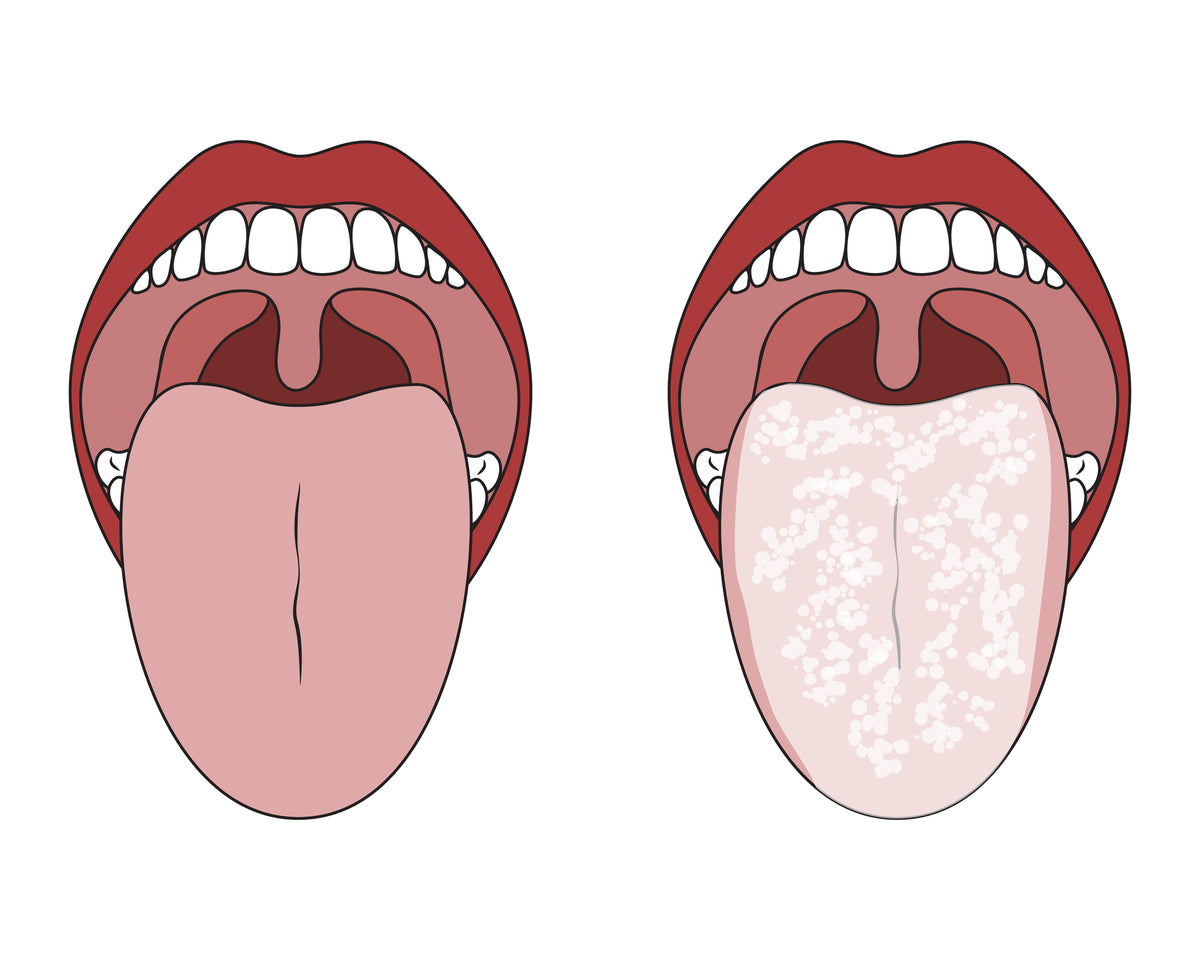
Several factors play a significant role in influencing the growth and spread of thrush-causing bacteria. One key factor is the environment in which the bacteria reside.
Thrush-causing bacteria thrive in warm, moist environments, such as the mouth, throat, and genital areas. These conditions provide the perfect breeding ground for the bacteria to proliferate and spread.
Additionally, certain lifestyle factors can also impact the growth of thrush-causing bacteria. Poor oral hygiene, a weakened immune system, and the use of antibiotics can all contribute to the overgrowth of these harmful bacteria.
Understanding these factors is essential in preventing and treating thrush infections effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the lifecycle of thrush-causing bacteria is crucial in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies for this common horse ailment. By identifying the environmental factors that contribute to bacterial growth and spread, horse owners can take proactive measures to keep their equine companions healthy and hoof thrush-free.
Regular hoof care, proper stable management, and timely intervention with appropriate treatments, such as Horse Thrush Treatment, are essential in combating thrush-causing bacteria and promoting overall hoof health in horses. By staying informed and proactive, horse owners can help prevent the detrimental effects of thrush and ensure their horses remain sound and comfortable.